What Is An Atomic Swap?
- Slava Jefremov
- Sep 9, 2025
- 5 min read
Updated: Dec 8, 2025

Key Takeaways
Atomic swaps enable trustless, P2P crypto exchanges across blockchains without intermediaries.
They originated in 2013, with the first successful swap executed in 2017 by Litecoin’s founder Charlie Lee.
Powered by HTLCs, atomic swaps guarantee fair, secure, and decentralized execution.
Benefits include decentralization, security, interoperability, and lower costs.
Drawbacks include technical complexity, lack of fiat support, and limited platform availability.
While atomic swaps enhance privacy, transactions remain visible on public blockchains.
Compared to cross-chain bridges, atomic swaps offer greater decentralization but less accessibility.
Introduction
The cryptocurrency industry was founded on the principles of decentralization, privacy, and user sovereignty. However, centralized exchanges (CEXs) — while convenient and widely used — have introduced challenges such as custodial risks, regulatory hurdles, and high fees. To address these inefficiencies, the concept of atomic swaps emerged as a powerful alternative, enabling trustless, peer-to-peer (P2P) exchanges across different blockchains.
This article explores atomic swaps in detail: their history, how they work, their advantages and disadvantages, and how they compare with cross-chain bridges. By the end, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of why atomic swaps are viewed as a cornerstone technology in decentralized finance (DeFi).
What Are Atomic Swaps?
Atomic swaps remove intermediaries and centralized control, making cryptocurrency exchanges more decentralized and secure.
They enable P2P transactions between individuals holding different cryptocurrencies across separate blockchains, eliminating the need for intermediaries such as Coinbase or Binance. These swaps are powered by self-executing smart contracts that automatically enforce trade conditions.
In contrast, centralized exchanges (CEXs) function much like stock markets: they manage liquidity, maintain order books, and connect buyers with sellers. However, CEXs are custodial — they hold users’ funds and private keys — which contradicts the decentralized ethos of blockchain.
This is where decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and atomic swaps shine. By fostering interoperability between blockchain networks, atomic swaps promote a true DeFi ethos: trustless, transparent, and user-controlled.
The Importance of Atomic Swaps
Atomic swaps solve inefficiencies inherent in centralized finance (CeFi) while unlocking seamless DeFi trading.
For example, suppose a user wants to exchange Ether (ETH) at $4,358 on the Ethereum network for Bitcoin (BTC) at $112,980 on the Bitcoin network using a CEX like Binance or Coinbase. The process typically involves:
Registering on the exchange (with KYC requirements).
Transferring ETH into the platform.
Converting ETH into BTC, incurring transaction fees and delays.
Withdrawing BTC into a personal wallet, often paying additional fees.
Waiting for confirmation and settlement.
This multistep process introduces unnecessary delays, high costs, and custodial risks. CEXs store assets in custodial wallets, leaving them vulnerable to hacks, freezes, or regulatory actions.
Atomic swaps bypass all of this. They eliminate intermediaries, cut down on fees, and reduce security risks by ensuring users always control their private keys.
A Brief History of Atomic Swaps
The foundations of atomic swaps trace back over a decade:
2012: Developer Sergio Demián Lerner created the first draft of a trustless exchange protocol.
2013: Tier Nolan published a comprehensive paper describing the atomic swap process, earning recognition as the pioneer of the technology.
2017: The first real-world implementation took place when Charlie Lee, the founder of Litecoin, tweeted about successfully performing an LTC/BTC swap. He exchanged Litecoin (LTC) at $113.89 for BTC.
Since then, platforms such as AtomicDEX, Lightning Network, and Liquality have adopted atomic swaps, paving the way for greater blockchain interoperability.
How Do Atomic Swaps Work?
Atomic swaps are powered by hashed timelock contracts (HTLCs), a type of smart contract that ensures trustless execution.
Atomic principle: A swap is either completed successfully or not executed at all. No partial or failed trades exist.
Smart contracts: Both parties must meet predetermined conditions before funds are released.
Hashlock: This mechanism locks the contract with a unique cryptographic key. Only when both parties reveal the key is the trade finalized.
Timelock: Sets a deadline for completion. If the trade isn’t executed within the time frame, funds are returned to their original owners.
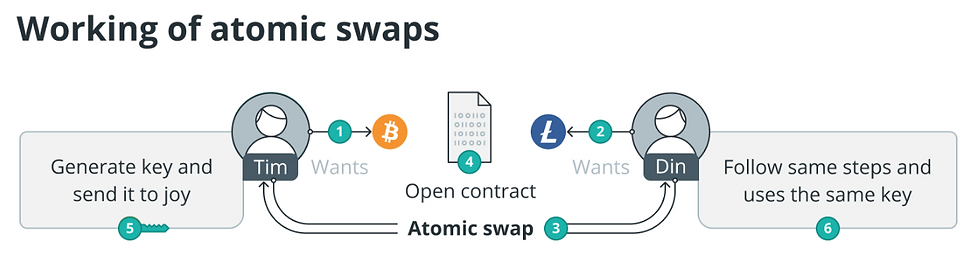
This structure guarantees fairness, removes reliance on third parties, and ensures both traders are protected.
Advantages of Atomic Swaps
Atomic swaps introduce multiple benefits:
Decentralization: Users trade directly without depending on a centralized liquidity pool.
Enhanced security: Hashlock and timelock mechanisms ensure funds are safe in case of delays or disputes.
Interoperability: Traders can swap across multiple blockchains, including altcoins that are often unsupported on CEXs.
Cost savings: Eliminating intermediaries reduces fees, making trades more efficient.
Disadvantages of Atomic Swaps
Despite their promise, atomic swaps face challenges:
Complexity: They require cryptographic knowledge and technical understanding, which can be intimidating for beginners.
Slow adoption: Few platforms currently support atomic swaps, limiting accessibility.
No fiat support: Unlike CEXs, atomic swaps cannot bridge directly between crypto and fiat.
Network delays: Blockchain wait times can slow down the process compared to centralized trading.
Nonetheless, as wallets and DEX platforms continue to evolve, atomic swaps are expected to become more user-friendly and widely adopted.
Can Atomic Swaps Be Tracked?
Atomic swaps are designed to maximize anonymity. Unlike CEXs, they do not require KYC verification. However, the underlying blockchains — Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, etc. — are public ledgers, meaning all transactions remain visible.
While the atomic swap itself blends into regular blockchain activity, individual transfers can still be traced. For enhanced privacy, users often rely on:
Coin mixing: Combining multiple transactions to obscure origins.
Privacy coins: Cryptocurrencies like Monero (XMR at $236.84) and Zcash (ZEC at $50.02) offer built-in anonymity that can be paired with atomic swaps.
Atomic Swaps vs. Cross-Chain Bridges
Both atomic swaps and cross-chain bridges enhance blockchain interoperability, but they function differently:
Atomic swaps: Direct, P2P exchanges of cryptocurrencies across blockchains. No wrapped tokens, no intermediaries.
Cross-chain bridges: Act as intermediaries that lock or burn tokens on one chain and mint wrapped tokens on another. For example, a wrapped BTC token can be used on Ethereum.
Cross-chain bridges are often easier for beginners due to their user-friendly interfaces. However, they reintroduce intermediary risks that atomic swaps were designed to eliminate.
Conclusion
Atomic swaps represent a major step toward a truly decentralized financial ecosystem. By eliminating intermediaries and empowering users with full custody of their assets, they align with the core philosophy of blockchain technology. Although adoption is still limited due to technical complexity, the future integration of atomic swaps into mainstream wallets and platforms is highly likely. As crypto trading evolves, atomic swaps may become the gold standard for secure, decentralized, and borderless asset exchange.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an atomic swap in simple terms?
An atomic swap allows two people to exchange cryptocurrencies directly from their wallets across different blockchains, without using a centralized exchange.
Do atomic swaps require fees?
While atomic swaps eliminate exchange fees, users may still pay standard blockchain transaction fees.
Can I swap crypto for fiat using atomic swaps?
No. Atomic swaps only work between cryptocurrencies. Converting to fiat still requires centralized platforms.
Are atomic swaps safe?
Yes. They use hashlock and timelock mechanisms to ensure funds are either exchanged successfully or returned to the original owner.
Can transactions from atomic swaps be traced?
While atomic swaps don’t reveal user identities, all transactions occur on public blockchains. Additional privacy tools like Monero or Zcash can enhance anonymity.



Comments